The feeling of heavy legs is associated with poor blood circulation in the veins. It manifests itself through bloated legs, tingling etc. Nutreov offers solutions that help you to combat the feeling of heavy legs to recover tonicity and lighter legs.
Vitality, energy and dynamism allow you to get the most out of life. Maintaining your energy levels is therefore essential. Nutreov offers solutions for restoring vitality, energy and dynamism in all circumstances.
Hot flushes, night sweats, fatigue, irritability, sleep disorders and vaginal dryness are just some of the symptoms of the menopause. Nutreov has developed solutions suited to the needs of everyone for counteracting menopausal discomfort.
Whether due to a poor diet, overweight or various chronic diseases, excess bad cholesterol (LDL) may lead to cardio-vascular diseases. Nutreov offers a formula composed of black garlic, vitamins and selenium to help maintain normal blood cholesterol.
A reduced efficiency of the immune system can lead to an increasing sensitivity to these attacks. Nutreov helps you to strengthen your immune defences thanks to effective and complete formulas.
The intestinal microbiota which plays a key role on different levels: digestive, metabolic, immune system and even neurological. Nutreov offers solutions suited to the needs of everyone to preserve your overall balance and strengthen your immune defences.
In particular, age, intense physical activity, overweight and lack of physical activity can weaken the joints. Nutreov offers solutions suited to the needs of everyone for reducing joint and muscular discomfort and thus regaining a better quality of life.
Stress, overwork, fatigue and insufficient rest are just some of the factors that can disrupt concentration and memory and which can undermine our intellectual capacities. Nutreov offers a specially formulated formula for boosting the memory and concentration.
A sore throat and difficulties breathing are symptoms that should not be disregarded so as to prevent eventual complications from developing that could be quite serious. Nutreov offers a solution to improve respiratory comfort whilst strengthening the body’s resistance.
Stress and sleep are intricately linked and create a vicious circle: stress can have a detrimental effect on the quality and duration of sleep, while insufficient sleep can increase stress levels. Nutreov offers solutions suited to the needs of everyone for restoring the balance essential for restorative sleep and thus reducing stress and nervousness.
There are many problems associated with digestion that can be detrimental to both your health and quality of life. Nutreov offers numerous formulas that provide solutions suited to the needs of everyone to improve intestinal transit and counteract digestive problems.
Urinary comfort has a significant impact on overall well-being. Nutreov offers formulas which facilitate the management of urinary discomfort at any time of life.
Stress and a poor diet are some of the factors which disrupt the body's healthy functioning. Nutreov offers draining and detoxifying products which help you to regain your ideal weight.
The demands of contemporary life do not always allow us to maintain a healthy and balanced diet. Nutreov offers a detoxifying solution which helps to restore a balanced metabolism.
Lack of exercise and an overly rich diet often lead to weight gain. Nutreov offers products that allow you to eliminate excess fats and water, whilst refining the silhouette.
It is not always easy to resist temptations and food cravings…Nutreov offers products which help to moderate the appetite and eliminate fats to help you regain your ideal weight.
Losing weight is not always easy. This is why Nutreov offers solutions suited to the objectives of everyone to help you regain your ideal weight.
Hair beauty is an attribute that should be maintained. Nutreov offers products that reduce hair loss and which nourish the hair from the inside.
Skin beauty is an attribute that should be maintained throughout life. Nutreov offers products suited to different stages of life to help you maintain firm and well hydrated skin.
To obtain a gorgeous tan, prepping the skin in advance is key. Nutreov offers products that allow all skin types to obtain an even and gorgeous tan.
Ail Noir® is a unique formula which helps to maintain a normal cholesterol level naturally.
The active ingredients selected for the Calori-Track® range bind fats, sugars and calories to successfully combat overweight.
The Capileov® range offers an exclusive complex which slows down hair loss, stimulates regrowth and strengthens the hair’s vitality.
Circuveinol® ensures enhanced circular action and promotes microcirculation.
With a natural formula based on 9 plant-based active ingredients, ColonPure® offers a gentle plant-based detox treatment.
Cramp®control is an optimum formula that allows for effective muscle relaxation.
The Cys-régul® range provides an adapted and effective response to this discomfort thanks to cranberry and D-Mannose, combined with plants with diuretic effects for quick action.
Détox Universel provides a liver-intestines-kidneys triple-action effect activating overall detox while reinforcing the toxin elimination process.
Fortigénor® is an anti-fatigue complex which improves mental and physical capacities in case of exhaustion and loss of concentration.
Immunea is a range which helps to strengthen the immune systems of both children and adults, while helping to reduce tiredness, thanks to a unique and complete complex which combines plants, vitamins, minerals and microbiotic strains.
Containing a plant fibre complex, solutions from the Laxeov® range improve intestinal transit in adults and children aged 3 years upwards naturally.
The Magné®control range offers the most complete magnesium-based solutions.
Taking overall account of disorders related to the menopause, the products from the Ménophytea® Équilibre range is of practical assistance to women who wish to recover their natural balance.
The Ménophytea® Intimité range meets the needs of women looking for comfort, relief and peace of mind.
The Ménophytea® Silhouette range provides effective aid for alleviating the effects of age on the mature female form supporting them throughout the menopause.
Composées d'actifs d'origine naturelle et de vitamines, nos formules NoStress® sont spécialement conçues pour apaiser votre esprit, renforcer votre résilience au stress et améliorer votre concentration.
Libérez-vous des tensions et vivez chaque jour avec sérénité grâce à NoStress®.
Difficulties in falling asleep, nocturnal awakenings, there are numerous sleep disruptions to which the Optinuit® range provides a suitable response without causing dependence.
The Pectiligne® range provides effective assistance for people wishing to better control their appetites.
Phytalgic®, 1st complete range for the treatment of joint problems, provides a natural aid tailored to individual problems.
With its trio of concentrated plants, boosted by essential oil of peppermint, the Phyto-Rub® range helps to relieve respiratory problems.
The intestinal microbiota which plays a key role on different levels: digestive, metabolic, immune system and even neurological. The Profidus® range provides solutions for the well-being of both children and adults thanks to its exclusive formulas, based on symbiotic complexes.
Skinsublim® is a complete and specialised range that helps to improve the beauty of the skin from the inside out.
Intended for those wishing to slim or control their weight, Slim Success® is a range that allows you to watch your weight.
With Sojyam®, laboratoires Nutreov offers a solution clinically proven to be effective for helping women to cope with their menopause better.
No time to follow a long-term diet plan? Looking for a quick and effective treatment? The Speed range was especially designed for those wishing to obtain quick results from their diet plan.
There are times in life that demand extra energy. A number of active ingredients well known for their energy boosting properties can be found in nature. Stim e®, offers a genuine concentrate of nature.
Highly concentrated in hive products, plants and vitamins, the solutions from the Stim® Royal range help to strengthen our bodies for a lasting anti-fatigue effect.
With Sunsublim®, laboratoires Nutreov offers a complete and expert range to suit every skin phototype.
The Triolinum® range offers solutions suited to various disorders related to the menopause thanks to compete natural and effective formulas.
The WaterPill® range meets specific needs related to slimming such as the reduction of water retention or cellulite.
There are several types of radiation: visible light, infrared and UV rays that are most harmful to our skin and body. UV rays are divided into two categories: UVA and UVB. UVAs penetrate further into the skin, up to the dermis. They are responsible for allergies and skin ageing. UVBs are stopped by the epidermis but are the cause of burning and sunburn.
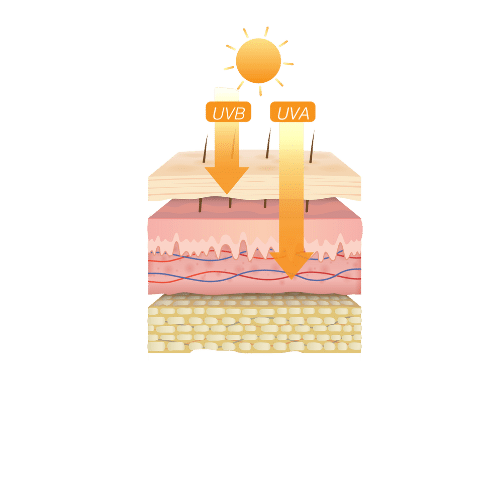
To overcome this problem of aggressive radiation and protect our skin and our bodies, it is necessary to learn about photoprotection (i.e. all the means available to act as a barrier to UV rays).


Artificial photoprotection

Choosing the right sunscreen means knowing your phototype well. But what is a phototype?
We need to start with pigmentation to understand how it is formed. In the epidermis, melanocytes produce melanin, a pigment that exists in two forms: eumelanin (brown-black) and pheomelanin (yellow-red). The distribution of these two types of pigment defines our phototype and therefore the colour of our skin, eyes and hair.

Very white skin. Blond – red hair. Blue or green eyes.
Do not tan. Systematic sunburn.

Matte skin. Brown or black hair Dark eyes.
Tan well. Little sunburn.

Fair skin. Blond or brown hair. Light or brown eyes.
Tan a little. Frequent sunburn.

Dark brown skin. Black hair. Black eyes.
Tan a lot. Rarely has sunburn.

Intermediate skin. Brown or brown hair. Brown eyes.
Tan regularly. Occasional sunburn.

Black skin. Black hair. Black eyes.
Tan a lot. Exceptional sunburn.
Knowing how the sun’s rays work, your phototype and the different types of photoprotection is the best way to enjoy the sun and make the most of your summer without putting yourself at risk.
But before the first summer rays, it is also possible to anticipate and prepare our body for this intense exposure.
Sun care supplements make it possible for the skin to prepare. It will then be more resistant to UVA and UVB rays. The formulas used in these dietary supplements will also improve skin hydration and slow down the ageing of the skin. From an aesthetic point of view, taking them in advance gives the skin a more even tan which, moreover, will last longer.
What provides all these beneficial actions for our skin and our body? What is found in Nutreov dietary supplements?

Natural pigments that lightly colour the skin and give an even tan.

Vitamin C, which contributes to better elasticity of the skin. This is because it is rich in collagen (a fibre found in the dermis).

Precious oils (evening primrose, argan, safflower) that help moisturise the skin.

Vitamin E, which has antioxidant action and thus contributes to the protection of cells.

Selenium, which supports vitamin E and reinforces the antioxidant action of dietary supplements.
As you can see, there’s no need to shun the sun – it’s good and enjoyable – you just need to know how to protect yourself from it. Hats, sunglasses, creams and food supplements are all essential to protect your body and make the most of the sun’s rays all summer long!
☀️ Préparez l’été avec les Soldes NUTREOV☀️ Dismiss